Learn English
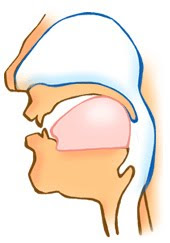
Production of the velar nasal: The vocal cords vibrate, and the velum is lowered so that the air escapes through the nose. The back of the tongue is raised so as to form a closure on the velum.
Pronunciation of
as in
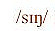
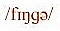
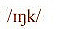
- 4.1.2 Alveolar
The Alveolar Nasal Production of the alveolar nasal /n/ : The vocal cords vibrate, and the velum is lowered so that the air has to escape through the nose. The tip and front of the tongue form a complete closure against the teeth ridge throughout the...
- 4.1.1 Bilabial
The Bilabial Nasal Production of the bilabial nasal /m/ : The vocal cords vibrate, and the velum is lowered so that the air escapes through the nose. The lips form a complete closure throughout the production phase. Pronunciation...
- 4.1 Nasals
Nasals Nasal sounds are formed with complete oral closure, lasting throughout the production phase. This means that the air has to be let out through the nose. The quality of the sound, however, relates to the mouth closure, and definitions are therefore...
- 4. Consonants
Consonants The diagramme shows the 24 consonant phonemes of Standard British English, divided into four groups. The groups are arranged according to degree of closure of the vocal organs. The Nasals and Stops are produced with complete oral closure, the...
- 3. Teaching Units
Teaching Units The diagramme lists the six groups of sounds that will be described in this course. Two of these belong to the vowel category, i.e. monophthongs and diphthongs, four are consonants. Note that the term vowel is used here for stable sounds...
Learn English
4.1.3 Velar
The Velar Nasal
Production of the velar nasal: The vocal cords vibrate, and the velum is lowered so that the air escapes through the nose. The back of the tongue is raised so as to form a closure on the velum.

Pronunciation of
as in
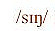
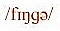
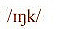
- 4.1.2 Alveolar
The Alveolar Nasal Production of the alveolar nasal /n/ : The vocal cords vibrate, and the velum is lowered so that the air has to escape through the nose. The tip and front of the tongue form a complete closure against the teeth ridge throughout the...
- 4.1.1 Bilabial
The Bilabial Nasal Production of the bilabial nasal /m/ : The vocal cords vibrate, and the velum is lowered so that the air escapes through the nose. The lips form a complete closure throughout the production phase. Pronunciation...
- 4.1 Nasals
Nasals Nasal sounds are formed with complete oral closure, lasting throughout the production phase. This means that the air has to be let out through the nose. The quality of the sound, however, relates to the mouth closure, and definitions are therefore...
- 4. Consonants
Consonants The diagramme shows the 24 consonant phonemes of Standard British English, divided into four groups. The groups are arranged according to degree of closure of the vocal organs. The Nasals and Stops are produced with complete oral closure, the...
- 3. Teaching Units
Teaching Units The diagramme lists the six groups of sounds that will be described in this course. Two of these belong to the vowel category, i.e. monophthongs and diphthongs, four are consonants. Note that the term vowel is used here for stable sounds...
