Learn English
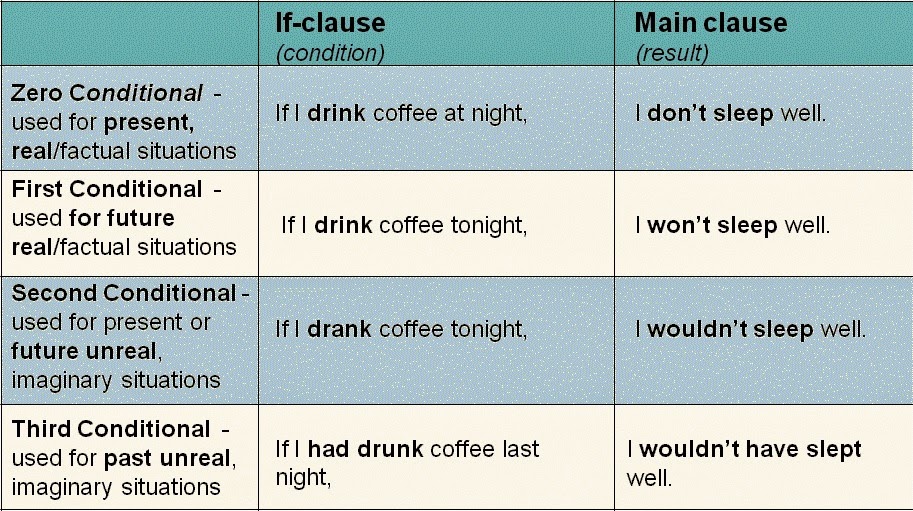
Conditional Clause and Main Clause
First, Second, and Third Conditional
Remember!
- Day 15
...
- Uses Of Some Important Conjunction
"No /not/never"??. "Or" If, no/not/never come in any sentence and after the whole cause, to joint that cause we will use or, not nor?like.. They have no relation or supporters who can help them.She has not a relative or supporter who can support her.I...
- Conditional Sentences. Part 2: Unreal Conditionals. If I Were A Rich Man...
A conditional sentence describes a condition that is necessary for a particular result to occur. If the weather is fine this weekend, I´ll go skiing. I.e. I´ll go skiing on condition that the weather is fine this weekend. There are different...
- Friend Wants To Buy A Car - English Conversation
TEENA: Ronny, what happened to you? You didn't come to office yesterday. I called and your phone was switched off. RONNY: Actually my car broke down on the way. TEENA: You could have come...
- Learning Nouns In English
A noun is the name of a person, place, thing or quality. Nouns are divided into five parts: 1. Proper Nouns 2. Common Nouns ...
Learn English
Conditional (If) Clauses Grammar Explanation and Sentences
English learners often have problems with conditional sentences. One problem is knowing which conditional to use. We may then have difficulties with the construction of the first, second or third conditional sentence.
Here are all four conditional forms in English, with examples and explanations of when and how to use them.
Zero conditional
If people eat too much, they get fat.
Zero conditional ? examples, structure, usage
If people eat too much, they get fat.
Zero conditional ? examples, structure, usage
First conditional
If I have time, I will visit you.
First conditional ? examples, structure, usage
If I have time, I will visit you.
First conditional ? examples, structure, usage
Second conditional
If I had more time, I would travel the world.
Second conditional ? examples, structure, usage
If I had more time, I would travel the world.
Second conditional ? examples, structure, usage
Third conditional
If I had had time, I would have gone to the football match.
Third conditional ? examples, structure, usage
If I had had time, I would have gone to the football match.
Third conditional ? examples, structure, usage

Conditional Clause and Main Clause
If I have enough money, conditional clause | I will go to Japan. main clause |
I will go to Japan, main clause | if I have enough money conditional clause |
First, Second, and Third Conditional
1. First conditional: | If I have enough money, I will go to Japan. |
2. Second conditional: | If I had enough money, I would go to Japan. |
3. Third conditional: | If I had had enough money, I would have gone to Japan. |
Conditional clause | Main clause |
1. If + Present Tense | will + inf / present tense / imperative |
a. If you help me with the dishes (if + pres), I will help you with your homework. (will + inf) b. If the sum of the digits of a number is divisible by three, the number is divisible by three (Pres. tense) c. If you see Mr Fox tonight, tell him I am ill. (imperative). | |
2. If + Past Tense | would + inf |
3. If + Past Perfect Tense | would have + past participle |
We do not normally use will or would in the conditional clause, only in the main clause. | |
Uses of the Conditional
1. First conditional
a. Nature: Open condition, what is said in the condition is possible.
b. Time: This condition refers either to present or to future time.
e.g. If he is late, we will have to go without him.
If my mother knows about this, we are in serious trouble.
e.g. If he is late, we will have to go without him.
If my mother knows about this, we are in serious trouble.
2. Second conditional
a. Nature: unreal (impossible) or improbable situations.
b. Time: present; the TENSE is past, but we are talking about the present, now.
e.g. If I knew her name, I would tell you.
If I were you, I would tell my father.
e.g. If I knew her name, I would tell you.
If I were you, I would tell my father.
Compare: If I become president, I will change the social security system. (Said by a presidential candidate)
If I became president, I would change the social security system. (Said by a schoolboy: improbable)
If we win this match, we are qualified for the semifinals.
If I won a million pounds, I would stop teaching. (improbable)
3. Third conditional
a. Nature: unreal
b. Time: Past (so we are talking about a situation that was not so in the past.)
e.g. If you had warned me, I would not have told your father about that party.(But you didn't, and I have).
e.g. If you had warned me, I would not have told your father about that party.(But you didn't, and I have).
Remember!
1. The conditional construction does not normally use will or would in if-clauses. EXCEPTION: If will or would express willingness, as in requests, they can be used in if-clauses.
e.g. If you will come this way, the manager will see you now.
I would be grateful if you would give me a little help.
(= ± please, come this way; please, give me...)
2. For the second conditional, were replaces was:
If I were a rich man...
3. After if, we can either use "some(-one, -where...)" or "any(-one, -where...).
If I have some spare time next weekend....or :
If I have any spare time...
4. Instead of if not, we can use unless.
e.g. I'll be back tomorrow unless there is a plane strike.
He'll accept the job unless the salary is too low.
5.There is a "mixed type" as well, for the present results of an unreal condition in
the past:
If + Past Perfect - would + inf.
If you had warned me [then], I would not be in prison [now].
- Day 15
...
- Uses Of Some Important Conjunction
"No /not/never"??. "Or" If, no/not/never come in any sentence and after the whole cause, to joint that cause we will use or, not nor?like.. They have no relation or supporters who can help them.She has not a relative or supporter who can support her.I...
- Conditional Sentences. Part 2: Unreal Conditionals. If I Were A Rich Man...
A conditional sentence describes a condition that is necessary for a particular result to occur. If the weather is fine this weekend, I´ll go skiing. I.e. I´ll go skiing on condition that the weather is fine this weekend. There are different...
- Friend Wants To Buy A Car - English Conversation
TEENA: Ronny, what happened to you? You didn't come to office yesterday. I called and your phone was switched off. RONNY: Actually my car broke down on the way. TEENA: You could have come...
- Learning Nouns In English
A noun is the name of a person, place, thing or quality. Nouns are divided into five parts: 1. Proper Nouns 2. Common Nouns ...
