Learn English
The Vocal Organs
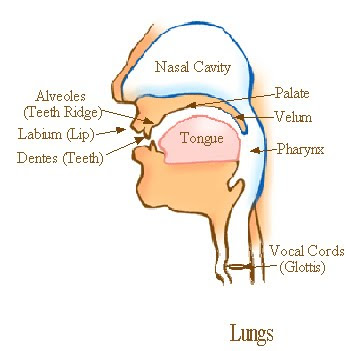
Speech is produced by the vocal organs. Every language has a definite set of speech sounds, and every sound can be described with reference to the vocal organ that is used to produce it. In this way sounds occurring in different languages can be compared, and foreign language learners can be helped to overcome pronunciation problems that arise from differences between languages. Knowledge of how the vocal organs function to produce the various sounds of a language will make near-native sound production possible.
Speech is produced by air from the lungs being processed or modified by all speech organs above the lungs: the glottis, pharynx, nose, tongue, and lips. The individual sound is identified by the closure or narrowing of these organs. If we see the tongue as the active articulator, the place which does not move can be called the passive articulator. Labels refer to the place where the closure or narrowing occurs, which means that the name normally refers to the passive articulator.
The speech sounds often have their names from the Latin name of the vocal organ:
- 4.2 Stops
Stops Stop sounds are produced with complete oral closure which is released quickly so as to end in an explosion or puff of air. If the release takes place slowly, the explosion ends in friction. This is regular for the Palatoalveolar sounds, but incidental...
- 4.1.3 Velar
The Velar Nasal Production of the velar nasal: The vocal cords vibrate, and the velum is lowered so that the air escapes through the nose. The back of the tongue is raised so as to form a closure on the velum. Pronunciation of as in ...
- 4.1.2 Alveolar
The Alveolar Nasal Production of the alveolar nasal /n/ : The vocal cords vibrate, and the velum is lowered so that the air has to escape through the nose. The tip and front of the tongue form a complete closure against the teeth ridge throughout the...
- 4.1 Nasals
Nasals Nasal sounds are formed with complete oral closure, lasting throughout the production phase. This means that the air has to be let out through the nose. The quality of the sound, however, relates to the mouth closure, and definitions are therefore...
- 4. Consonants
Consonants The diagramme shows the 24 consonant phonemes of Standard British English, divided into four groups. The groups are arranged according to degree of closure of the vocal organs. The Nasals and Stops are produced with complete oral closure, the...
Learn English
1. Sound production
The Vocal Organs
Speech is produced by the vocal organs. Every language has a definite set of speech sounds, and every sound can be described with reference to the vocal organ that is used to produce it. In this way sounds occurring in different languages can be compared, and foreign language learners can be helped to overcome pronunciation problems that arise from differences between languages. Knowledge of how the vocal organs function to produce the various sounds of a language will make near-native sound production possible.
Speech is produced by air from the lungs being processed or modified by all speech organs above the lungs: the glottis, pharynx, nose, tongue, and lips. The individual sound is identified by the closure or narrowing of these organs. If we see the tongue as the active articulator, the place which does not move can be called the passive articulator. Labels refer to the place where the closure or narrowing occurs, which means that the name normally refers to the passive articulator.
The speech sounds often have their names from the Latin name of the vocal organ:

Nasal sounds: through nose (velum down)
Oral sounds: through mouth (velum up)Stops: full oral closure
Fricatives: partial oral closure (friction)
Approximants: narrowing (no friction)
Labial: from labium, lip(s) active
Dental: from dentes, teeth active
Alveolar: Alveoles, teeth ridge active
Palatal: Palate, hard palate active
Velar: Velum, soft palate active
Glottal: Glottis, vocal cords active
Approximants: narrowing (no friction)
Labial: from labium, lip(s) active
Dental: from dentes, teeth active
Alveolar: Alveoles, teeth ridge active
Palatal: Palate, hard palate active
Velar: Velum, soft palate active
Glottal: Glottis, vocal cords active
- 4.2 Stops
Stops Stop sounds are produced with complete oral closure which is released quickly so as to end in an explosion or puff of air. If the release takes place slowly, the explosion ends in friction. This is regular for the Palatoalveolar sounds, but incidental...
- 4.1.3 Velar
The Velar Nasal Production of the velar nasal: The vocal cords vibrate, and the velum is lowered so that the air escapes through the nose. The back of the tongue is raised so as to form a closure on the velum. Pronunciation of as in ...
- 4.1.2 Alveolar
The Alveolar Nasal Production of the alveolar nasal /n/ : The vocal cords vibrate, and the velum is lowered so that the air has to escape through the nose. The tip and front of the tongue form a complete closure against the teeth ridge throughout the...
- 4.1 Nasals
Nasals Nasal sounds are formed with complete oral closure, lasting throughout the production phase. This means that the air has to be let out through the nose. The quality of the sound, however, relates to the mouth closure, and definitions are therefore...
- 4. Consonants
Consonants The diagramme shows the 24 consonant phonemes of Standard British English, divided into four groups. The groups are arranged according to degree of closure of the vocal organs. The Nasals and Stops are produced with complete oral closure, the...
