Learn English
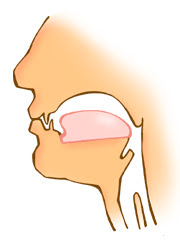
Bilabial stops are produced by the lower lip forming a closure with the upper lip, so that the air cannot escape. The sound occurs when the closure is abruptly released as a puff of air. The stop sounds occur in a pair, i.e. one Fortis and one Lenis realisation. The Fortis stop /p/ is never voiced, and there is generally a degree of devoicing of the Lenis sound as well when it is not surrounded by other voiced sounds. Devoicing is therefore most common in the end position of a word. The lenis stop will generally have a marked lengthening effect on the preceding sound(s).
/ p /
as in
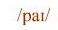
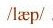
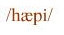
/ b /
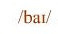
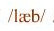

- 4.2 Stops
Stops Stop sounds are produced with complete oral closure which is released quickly so as to end in an explosion or puff of air. If the release takes place slowly, the explosion ends in friction. This is regular for the Palatoalveolar sounds, but incidental...
- 4.1.1 Bilabial
The Bilabial Nasal Production of the bilabial nasal /m/ : The vocal cords vibrate, and the velum is lowered so that the air escapes through the nose. The lips form a complete closure throughout the production phase. Pronunciation...
- 4. Consonants
Consonants The diagramme shows the 24 consonant phonemes of Standard British English, divided into four groups. The groups are arranged according to degree of closure of the vocal organs. The Nasals and Stops are produced with complete oral closure, the...
- 3. Teaching Units
Teaching Units The diagramme lists the six groups of sounds that will be described in this course. Two of these belong to the vowel category, i.e. monophthongs and diphthongs, four are consonants. Note that the term vowel is used here for stable sounds...
- 1. Sound Production
The Vocal Organs Speech is produced by the vocal organs. Every language has a definite set of speech sounds, and every sound can be described with reference to the vocal organ that is used to produce it. In this way sounds occurring in different languages...
Learn English
4.2.1 Bilabial
Bilabial Stops
Bilabial stops are produced by the lower lip forming a closure with the upper lip, so that the air cannot escape. The sound occurs when the closure is abruptly released as a puff of air. The stop sounds occur in a pair, i.e. one Fortis and one Lenis realisation. The Fortis stop /p/ is never voiced, and there is generally a degree of devoicing of the Lenis sound as well when it is not surrounded by other voiced sounds. Devoicing is therefore most common in the end position of a word. The lenis stop will generally have a marked lengthening effect on the preceding sound(s).

/ p /
as in
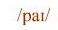
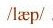
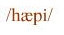
/ b /
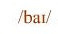
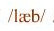

- 4.2 Stops
Stops Stop sounds are produced with complete oral closure which is released quickly so as to end in an explosion or puff of air. If the release takes place slowly, the explosion ends in friction. This is regular for the Palatoalveolar sounds, but incidental...
- 4.1.1 Bilabial
The Bilabial Nasal Production of the bilabial nasal /m/ : The vocal cords vibrate, and the velum is lowered so that the air escapes through the nose. The lips form a complete closure throughout the production phase. Pronunciation...
- 4. Consonants
Consonants The diagramme shows the 24 consonant phonemes of Standard British English, divided into four groups. The groups are arranged according to degree of closure of the vocal organs. The Nasals and Stops are produced with complete oral closure, the...
- 3. Teaching Units
Teaching Units The diagramme lists the six groups of sounds that will be described in this course. Two of these belong to the vowel category, i.e. monophthongs and diphthongs, four are consonants. Note that the term vowel is used here for stable sounds...
- 1. Sound Production
The Vocal Organs Speech is produced by the vocal organs. Every language has a definite set of speech sounds, and every sound can be described with reference to the vocal organ that is used to produce it. In this way sounds occurring in different languages...
